中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (7): 1057-1062.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.07.014
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
艾烟溶液干预人肺腺癌细胞活性氧和超氧化物歧化酶的活性
窦传字1,吴焕淦1,王硕硕2,马晓芃1,黄 艳1,赵继梦3,胡智海2,刘慧荣1,崔云华1,周次利1,赵 琛4
- 1上海中医药大学上海市针灸经络研究所,上海市 200030; 2上海中医药大学附属上海市中西医结合医院,上海市 200082; 3上海中医药大学,上海市 201203;4上海中医药大学针灸推拿学院,上海市 201203
Activities of reactive oxygen species and superoxide dismutase in human lung adenocarcinoma cells impacted by moxa smoke solution
Dou Chuan-zi1, Wu Huan-gan1, Wang Shuo-shuo2, Ma Xiao-peng1, Huang Yan1, Zhao Ji-meng3, Hu Zhi-hai2, Liu Hui-rong1, Cui Yun-hua1, Zhou Ci-li1, Zhao Chen4
- 2012031Shanghai Research Institute of Acupuncture and Meridian, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200030, China; 2Shanghai TCM-Integrated Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200082, China; 3Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China; 4Acupuncture and Tuina College, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
摘要:
背景:艾灸生成物的安全性研究是近年来灸法领域的关注热点,探讨艾烟成分对人体器官、组织、细胞的生物学效应是研究艾灸安全性的重要方向。研究表明艾烟溶液可引起肺泡Ⅱ型上皮细胞A549凋亡,但具体机制尚不清楚。
目的:观察艾烟采集物对肺泡Ⅱ型上皮细胞A549生长抑制率、细胞内活性氧、超氧化物歧化酶的影响,探讨艾烟采集物对A549的氧化损伤机制。
方法:采用便携式空气采样器采集艾条燃烧产生的烟气颗粒物,加入DMEM培养基分别配制质量浓度0.5,0.4,0.3,0.2,0.1,0.05,0.025,0.01 g/L的艾烟溶液干预A549细胞。采用细胞计数试剂盒(CCK-8)检测细胞生长抑制率,2',7'-二氯荧光黄双乙酸盐法观察细胞内活性氧信号强度,分光光度法测量并计算细胞超氧化物歧化酶活性。
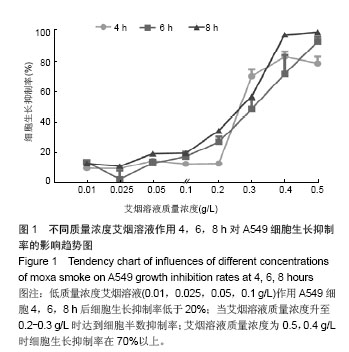
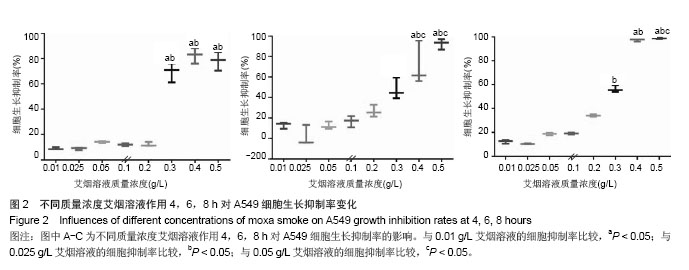
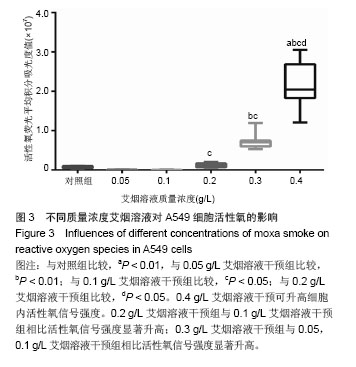
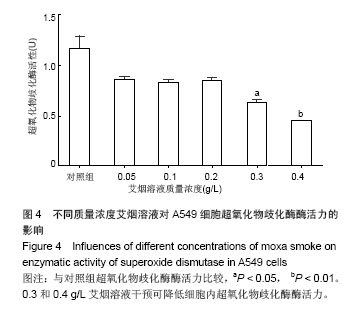
结果与结论:不同质量浓度艾烟溶液干预A549细胞4,6,8 h结果均显示,0.4,0.5 g/L艾烟溶液对A549细胞的生长抑制率高于0.01,0.025 g/L组(P < 0.05)。质量浓度0.05,0.1 g/L艾烟溶液可降低肺A549细胞内活性氧的含量,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);高质量浓度0.4 g/L艾烟溶液可增加肺A549细胞内活性氧水平(P < 0.01),降低超氧化物歧化酶活性(P < 0.01)。结果证实,艾烟对A549细胞具有生物学活性,对细胞的过氧化作用可能是高浓度艾烟溶液抑制A549细胞生长的重要机制。
中图分类号:
.jpg)